Azure Virtual IP Service
1. Public IP
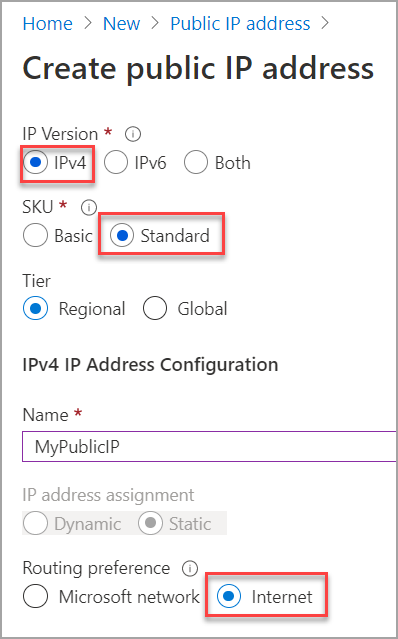
2. SKUs
All public IP addresses created before the introduction of SKUs are Basic SKU public IP addresses. You can't change the SKU after the public IP address is created.
A standalone virtual machine, virtual machines within an availability set, or Virtual Machine Scale Sets can use Basic or Standard SKUs. Mixing SKUs between virtual machines within availability sets or scale sets or standalone VMs isn't allowed.
Basic: Basic public IP addresses don't support Availability zones. The Availability zone setting is set to None by default if the public IP address is created in a region that supports availability zones.
Standard: Standard public IP addresses can be associated to Azure resources that support public IPs, such as virtual machines, load balancers, and Azure Firewall. The Availability zone setting is set to Zone-redundant by default if the IP address is created in a region that supports availability zones. For more information about availability zones, see the Availability zone setting.
The standard SKU is required if you associate the address to a standard load balancer. For more information about standard load balancers, see Azure load balancer standard SKU.
2.1. Location
Must exist in the same location, also referred to as region, as the resource to which you associate the public IPs.
3. IP configuration
-
Private and (optionally) public IP addresses are assigned to one or more IP configurations assigned to a network interface.
-
You can create many IP configurations for a NIC. Each IP configuration can be associated with a different public IP address.
4. Allocation methods
4.1. Dynamic
Dynamic addresses are assigned after a public IP address is associated to an Azure resource and is started for the first time. Dynamic addresses can change if a resource such as a virtual machine is stopped (deallocated) and then restarted through Azure. The address remains the same if a virtual machine is rebooted or stopped from within the guest OS. When a public IP address resource is removed from a resource, the dynamic address is released.
Dynamic private IPv4 and IPv6 (optionally) addresses are assigned by default.
4.2. Static
Static addresses are assigned when a public IP address is created. Static addresses aren't released until a public IP address resource is deleted.
5. Routing preference
By default, the routing preference for public IP addresses is set to Microsoft network. The Microsoft network setting delivers traffic over Microsoft's global wide area network to the user.
The selection of Internet minimizes travel on Microsoft's network. The Internet setting uses the transit ISP network to deliver traffic at a cost-optimized rate. A public IP addresses routing preference can’t be changed once created. For more information on routing preference, see What is routing preference (preview)?.
6. DNS name
Must be unique within the Azure location you create the name in across all subscriptions and all customers. Azure automatically registers the name and IP address in its DNS so you can connect to a resource with the name.
Azure appends a default subnet such as location.cloudapp.azure.com to the name you provide to create the fully qualified DNS name. If you choose to create both address versions, the same DNS name is assigned to both the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. Azure's default DNS contains both IPv4 A and IPv6 AAAA name records.