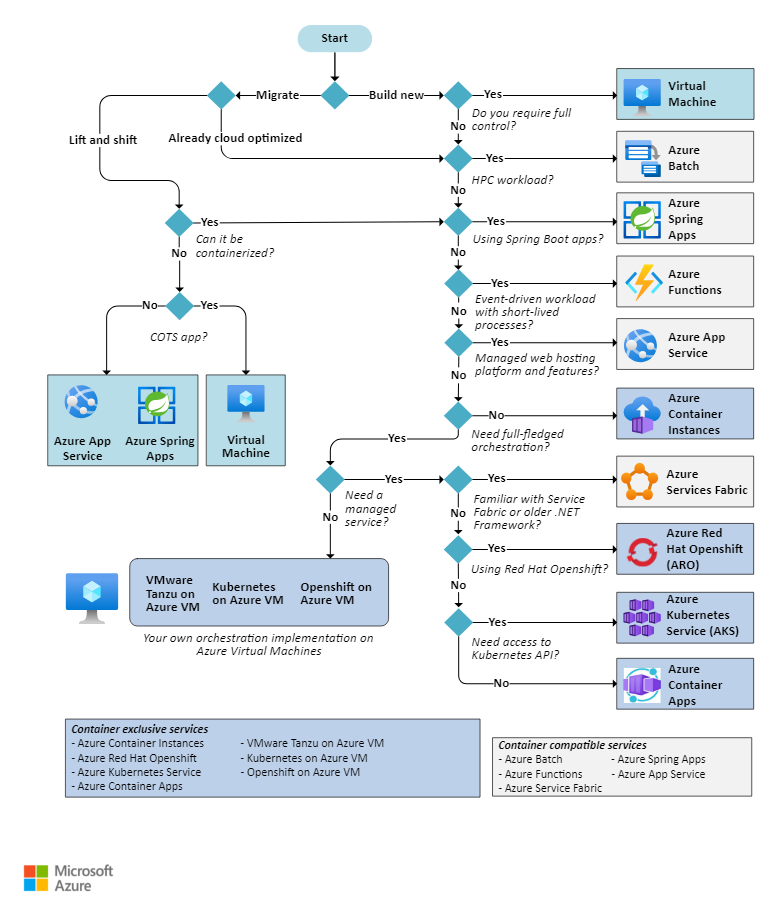
Azure Compute Service - Options
Understand the basic features
If you're not familiar with the Azure service selected in the previous section, see this overview documentation:
- Azure Virtual Machines: A service where you deploy and manage virtual machines (VMs) inside an Azure virtual network.
- Azure App Service: A managed service for hosting web apps, mobile app back ends, RESTful APIs, or automated business processes.
- Azure Functions: A managed function as a service. It's optimized for running event-driven applications using the functions programming model. The Azure Functions programming model provides productivity benefits for teams looking to trigger the execution of your functions on events and bind to other data sources.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): A managed Kubernetes service for running containerized applications.
- Azure Container Apps: A managed service built on Kubernetes, which simplifies the deployment of containerized applications in a serverless environment.
- Azure Container Instances: This service is a fast and simple way to run a container in Azure (a single pod of Hyper-V isolated containers on demand.). You don't have to provision any VMs or adopt a higher-level service. Concepts like scale, load balancing, and certificates aren't provided with ACI containers. For example, to scale to five container instances, you create five distinct container instances.
- Azure Red Hat OpenShift: A fully managed OpenShift cluster for running containers in production with Kubernetes.
- Azure Spring Apps: A managed service designed and optimized for hosting Spring Boot apps.
- Azure Service Fabric: A distributed systems platform that can run in many environments, including Azure or on-premises.
- Azure Batch: A managed service for running large-scale parallel and high-performance computing (HPC) applications.
Decision tree
References
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/guide/technology-choices/compute-decision-tree
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/container-instances/container-instances-best-practices-and-considerations