Azure App Service
1. Azure App Service
Azure App Service is an HTTP-based service for hosting web applications, REST APIs, and mobile back ends. You can develop in your favorite programming language or framework. Applications run and scale with ease on both Windows and Linux-based environments.
- The ability to scale up/down or scale out/in is baked into the Azure App Service.
- With Azure App Service, you can deploy and run containerized web apps on Windows and Linux.
- The Azure portal provides out-of-the-box continuous integration and deployment with Azure DevOps Services, GitHub, Bitbucket, FTP, or a local Git repository on your development machine.
- When you deploy your web app you can use a separate deployment slot instead of the default production slot when you're running in the Standard App Service Plan tier or better.
2. App Service Plan
In App Service, an app always runs in an App Service plan.
An App Service plan defines a set of compute resources for a web app to run. One or more apps can be configured to run on the same computing resources (or in the same App Service plan).
2.1. Plan configuration
| Plan | Free (F1) | Shared (D1) | Basic (B1, B2, B3) | Standard (S1, S2, S3) | Premium (P1V3, P2V3, P3V3) | Isolated (I1V2, I2V2, I3V2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Development/testing | Basic web apps | Small apps with low traffic | Production apps with higher traffic | Large-scale apps, high availability | Enterprise-level, large-scale apps | |
| Custom Domains | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| SSL Support | No | No | Yes (SNI SSL) | Yes (SNI + IP SSL) | Yes (SNI + IP SSL) | Yes (SNI + IP SSL) | |
| Auto-Scaling | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Daily CPU Minutes | 60 minutes | 240 minutes | Not applicable (dedicated) | Not applicable (dedicated) | Not applicable (dedicated) | Not applicable (dedicated) | |
| VM Size | Shared | Shared | Dedicated VM (1, 2, or 4 vCPUs) | Dedicated VM (1, 2, or 4 vCPUs) | Dedicated VM (up to 32 vCPUs in P3V3) | Isolated VM (up to 64 vCPUs) | |
| Storage | 1 GB | 1 GB | 10 GB | 50 GB | 250 GB | 1 TB | |
| Traffic | Limited | Limited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | |
| Custom TLS/SSL | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Virtual Network | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes (Private VNET) | |
| Cost | Free | Very Low Cost | Low cost | Moderate cost | High cost | Highest cost |
Key Features:
- Free Plan (F1): Great for basic testing, with no custom domain support. They are best for development, testing, or small-scale websites where downtime is acceptable.
- Shared Plan (D1): Affordable plan for small, low-traffic websites. They are best for development, testing, or small-scale websites where downtime is acceptable.
- Basic Plan (B1, B2, B3): Dedicated VMs for small-scale apps, no auto-scaling. the Basic tier does not come with an availability SLA. It is primarily suited for small applications that don’t require high availability guarantees.
- Standard Plan (S1, S2, S3): Adds auto-scaling, SSL, and more storage. Ideal for production workloads. This is suitable for production environments where moderate traffic is expected, and some degree of downtime is tolerable.
- Premium Plan (P1V3, P2V3, P3V3): High performance for large-scale apps, faster VMs, and better storage. The Premium plan also provides a 99.95% SLA for availability, but with better performance, more features, and higher resource allocation. Suitable for mission-critical apps with higher traffic and scalability needs.
- Isolated Plan (I1V2, I2V2, I3V2): Designed for enterprise apps needing dedicated VMs in a fully isolated environment with private networking. The Isolated plan offers an SLA of 99.95%, but if it’s deployed with Zone Redundancy (which distributes your app across different Azure availability zones), it can reach 99.99% availability. This makes it ideal for enterprise-level, high-availability apps.
This table should help compare the Azure App Service plans based on features, performance, and scalability.
2.2. Pricing tiers
- Shared compute: Free and Shared, the two base tiers, runs an app on the same Azure VM as other App Service apps, including apps of other customers, and can't scale out.
- Dedicated compute: The Basic, Standard, Premium, PremiumV2, and PremiumV3 tiers run apps on dedicated Azure VMs. Only apps in the same App Service plan share the same compute resources.
- Isolated: The Isolated and IsolatedV2 tiers run dedicated Azure VMs on dedicated Azure Virtual Networks. It provides network isolation on top of compute isolation to your apps. It provides the maximum scale-out capabilities. Isolate your app into a new App Service plan when:
- The app is resource-intensive.
- You want to scale the app independently from the other apps in the existing plan.
- The app needs resource in a different geographical region.
3. Scale
3.1. Scale out automatically
Automatic scaling is a new scale-out option that automatically handles scaling decisions for your web apps and App Service Plans. With automatic scaling, you can adjust scaling settings to improve your app's performance and avoid cold start issues.

3.2. Scale out with rules
Autoscale allows you to automatically scale your applications or resources based on demand. Use Autoscale to provision enough resources to support the demand on your application without over provisioning and incurring unnecessary costs.
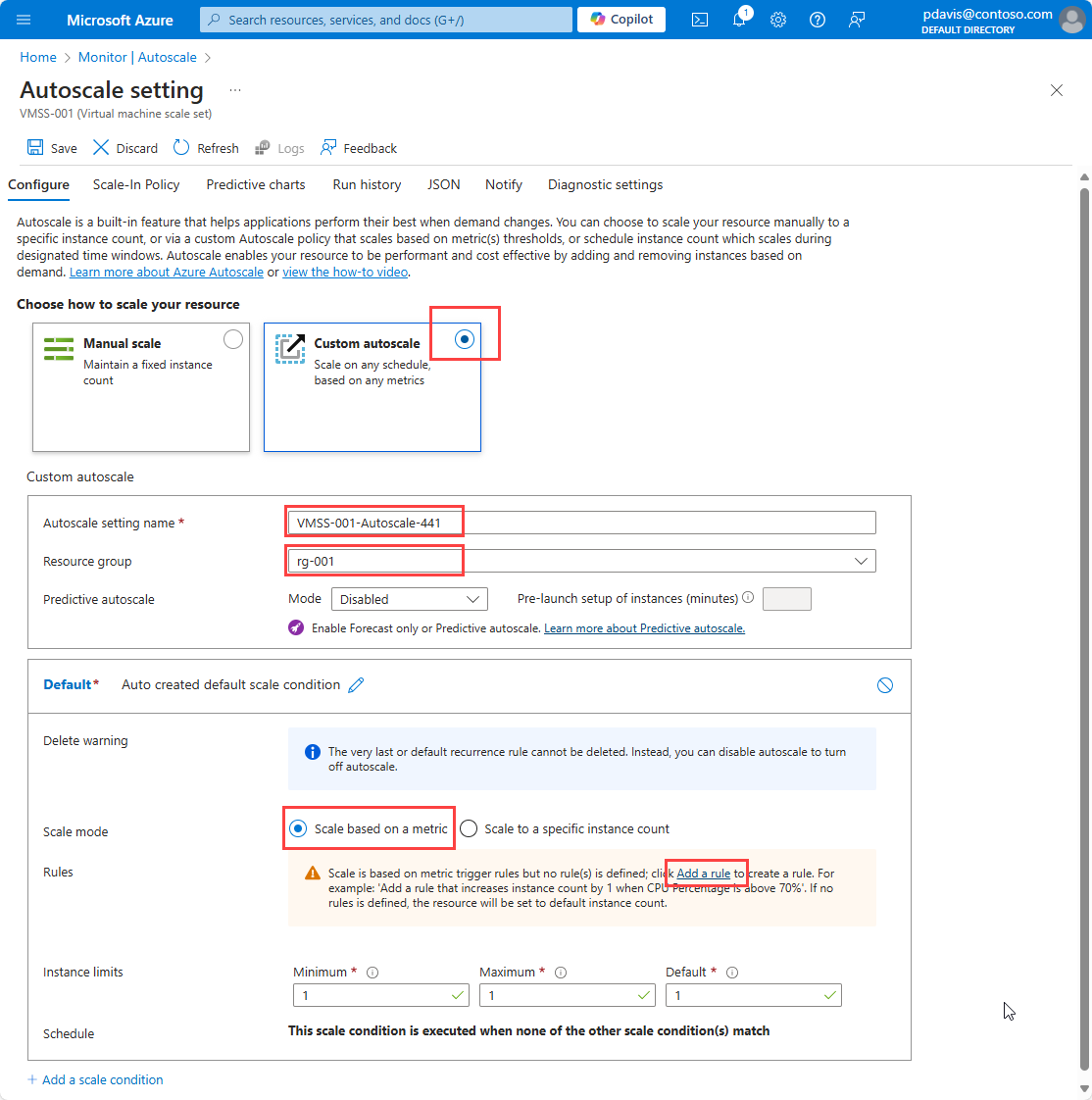
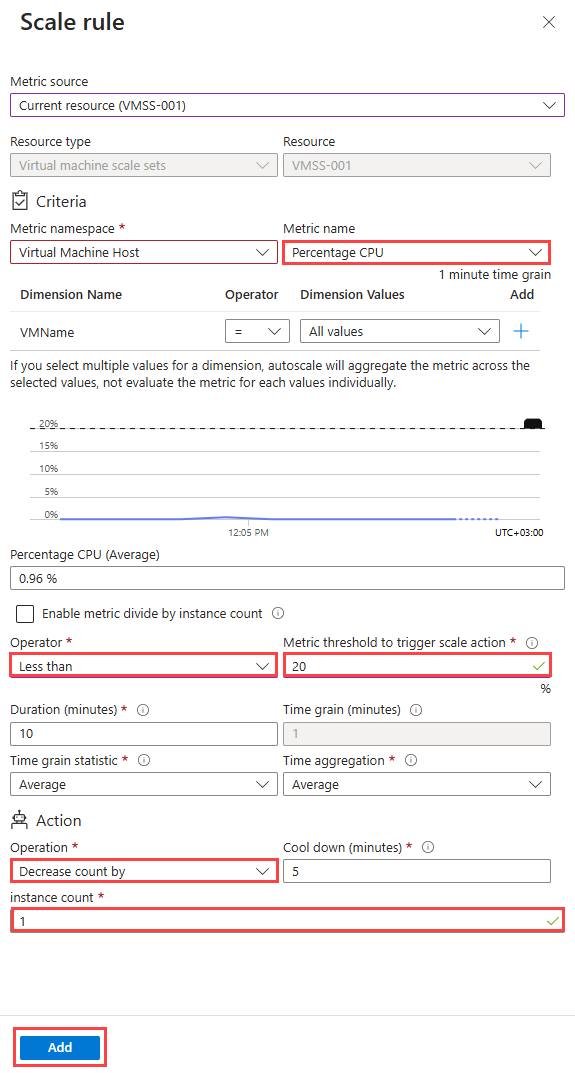
4. Automatic deployments
Azure supports automated deployment directly from several sources. The following options are available: - Azure DevOps services - Github - Bitbucket
5. Deployment slots
-
When using a Standard App Service Plan tier or better, you can deploy your app to a staging environment and then swap your staging and production slots.
-
The swap operation warms up the necessary worker instances to match your production scale, thus eliminating downtime.
6. Authentication & authorization
6.1. Built-in authentication
- Azure App Service allows you to integrate various auth capabilities into your web app or API without implementing them yourself.
- It’s built directly into the platform and doesn’t require any particular language, SDK, security expertise, or code.
- You can integrate with multiple login providers. For example, Microsoft Entra ID, Facebook, Google, X.
6.2. How it works
- Authenticates users and clients with the specified identity provider(s)
- Validates, stores, and refreshes OAuth tokens issued by the configured identity provider(s)
- Manages the authenticated session.
- Injects identity information into HTTP request headers
6.3. Some auth providers
| Provider | Sign-in endpoint | How-To guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft identity platform | /.auth/login/aad |
App Service Microsoft identity platform login |
/.auth/login/google |
App Service Google login | |
| GitHub | /.auth/login/github |
App Service GitHub login |
7. Azure App Service plan overview
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/overview-hosting-plans
8. App Service Environment overview
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/environment/overview
9. Reliability in Azure App Service
-
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/reliability/reliability-app-service?tabs=cli
-
https://learn.microsoft.com/training/modules/describe-high-availability-disaster-recovery-strategies/
10. Network
By default, apps hosted in App Service are accessible directly through the internet and can reach only internet-hosted endpoints.
11. Backup
- There are 2 types of backup: automatic (app) and custom (app & database)
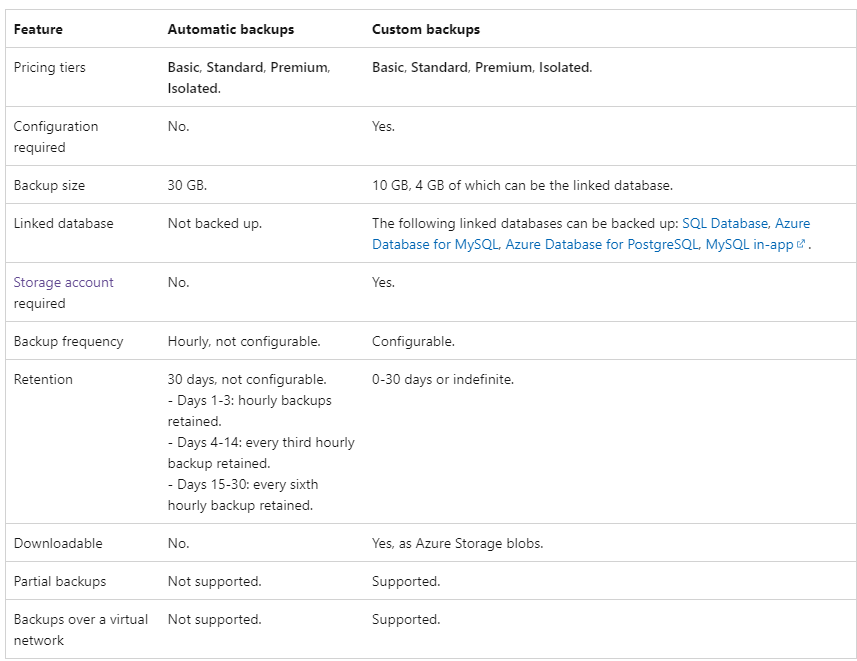
12. Restore
App Service stops the target app or target slot while restoring a backup. To minimize downtime for a production app, restore the backup to a deployment slot first, then swap into production.
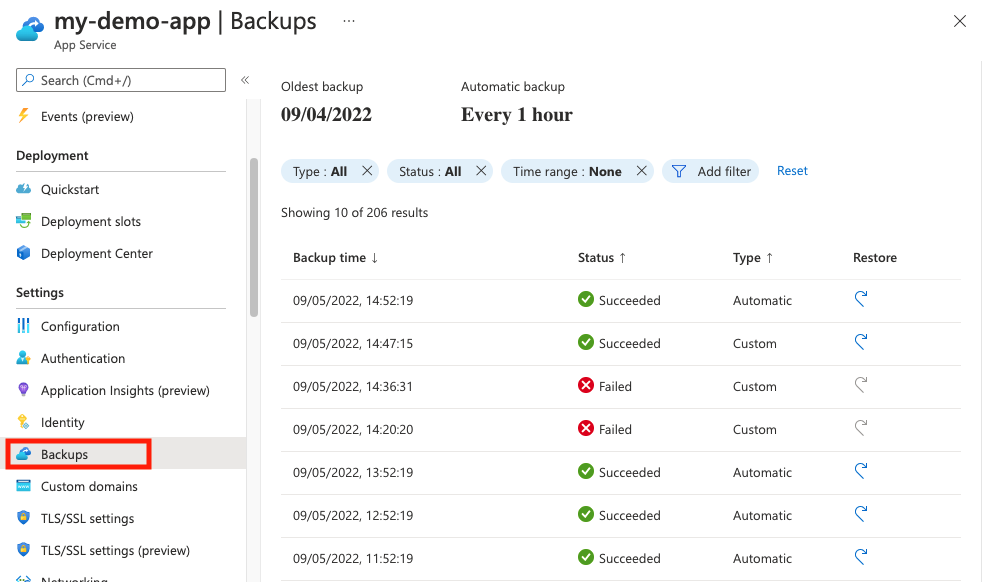
Select the restore option
13. References
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/training/modules/introduction-to-azure-app-service/2-azure-app-service
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/manage-backup?tabs=portal