Azure SQL Database
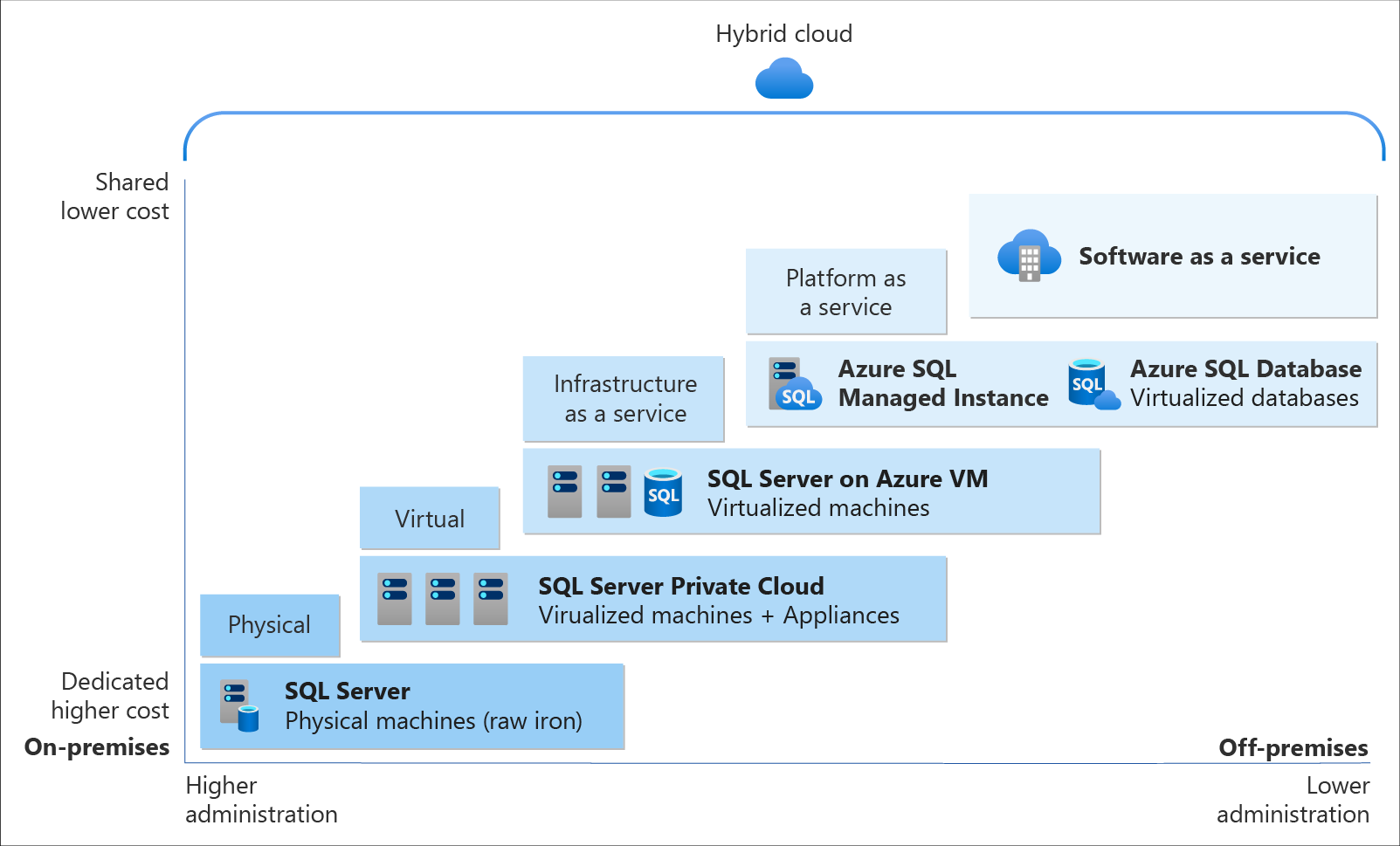
1. Different database solutions
Azure SQL is a family of managed, secure, and intelligent products that use the SQL Server database engine in the Azure cloud. Azure SQL is built upon the familiar SQL Server engine, so you can migrate applications with ease and continue to use the tools, languages, and resources you're familiar with. Your skills and experience transfer to the cloud, so you can do even more with what you already have.
The three products in the Azure SQL family are:
-
Azure SQL Database: Support modern cloud applications on an intelligent, managed database service that includes serverless compute.
-
Azure SQL Managed Instance: Modernize your existing SQL Server applications at scale with an intelligent fully managed instance as a service, with almost 100% feature parity with the SQL Server database engine. Best for most migrations to the cloud.
-
SQL Server on Azure VMs: Lift-and-shift your SQL Server workloads with ease and maintain 100% SQL Server compatibility and operating system-level access.
2. SSIS, SSAS, SSRS
- SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines is the only option to maintain SSIS, SSAS, and SSRS. SQL
- Managed Instance and Azure SQL Database do not support SSIS, SSAS, and SSRS.
- Azure Synapse Analytics does not support the SQL Server Database Engine, SSIS, and SSRS.
2.1. SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)
Integration Services can extract and transform data from a wide variety of sources such as XML data files, flat files, and relational data sources, and then load the data into one or more destinations.
2.2. SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS)
Analysis Services is an analytical data engine (VertiPaq) used in decision support and business analytics. It provides enterprise-grade semantic data models for business reports and client applications such as Power BI, Excel, Reporting Services reports, and other data visualization tools.
2.3. SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) provides a set of on-premises tools and services to create, deploy, and manage paginated reports. Download SQL Server 2022 Reporting Services from the Microsoft Download Center, and then install Reporting Services.
3. Encryption
Data exists in three basic states: data at rest, data in motion, and data in process.
-
Data at rest is data on a storage device that isn't being moved or used. Data at rest includes archived email messages stored in your Outlook inbox, or files on your laptop that you aren't using.
-
Data in motion (also called data in transit) is data that's being moved from one device to another within a private network or public network like the internet. data in motion can also be data that's being read (used) but not changed. Data in motion includes email messages in transit, browsing internet websites, or using company applications like an organization chart.
-
Data in process is data that's open and being changed. Data in process includes writing an email message, saving your work files, or ordering from a website.
There are different encryption methods for each of data state. The following table summarizes the methods.
Expand table
| Data state | Encryption method | Encryption level |
|---|---|---|
| Data at rest | Transparent data encryption (TDE) | Always encrypted. |
| Data in motion | Secure Socket Layers and Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) | Always encrypted. |
| Data in process | Dynamic data masking | Specific data is unencrypted. Remaining data is encrypted. |
| ### 3.1. Always encrypted |

Always Encrypted and Always Encrypted with secure enclaves are features designed to safeguard sensitive information, including credit card numbers and national or regional identification numbers (such as U.S. social security numbers), in Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and SQL Server databases. It enables clients to encrypt sensitive data within client applications, ensuring that encryption keys are never exposed to the Database Engine. This provides a separation between those who own the data and can view it, and those who manage the data but should have no access: on-premises database administrators, cloud database operators, or other high-privileged unauthorized users.
3.2. Transparent data encryption (TDE)
Transparent data encryption (TDE) encrypts SQL Server, Azure SQL Database, and Azure Synapse Analytics data files. This encryption is known as encrypting data at rest.
Encryption of a database file is done at the page level. The pages in an encrypted database are encrypted before they're written to disk and are decrypted when read into memory. TDE doesn't increase the size of the encrypted database.
With TDE with Azure Key Vault integration, users can control key management tasks including key rotations, key vault permissions, key backups, and enable auditing/reporting on all TDE protectors using Azure Key Vault functionality.
4. Disaster Recovery
| DR Solution | RPO | RTO | Failover Type | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Geo-Replication | ~5 seconds | <30 seconds | Manual failover | Global applications requiring quick recovery |
| Auto-Failover Groups | ~5 seconds | 30 seconds - few minutes | Automatic/manual failover | Applications needing automated cross-region DR |
| Zone Redundant Configuration | 0 (no data loss) | <30 seconds | Automatic failover within region | High availability within a region |
| Point-in-Time Restore | Up to 1 hour | Minutes to hours | Manual restore | Recovering from accidental data loss |
| Geo-Restore | Up to 1 hour | Several hours | Manual restore | Full region-wide disaster recovery |
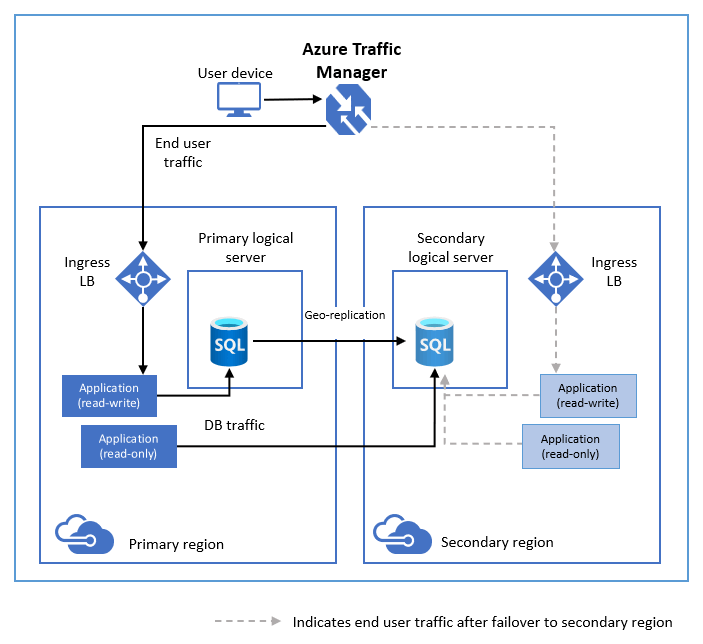
4.1. Active geo-replication
Active geo-replication is designed as a business continuity solution. Active geo-replication lets you perform quick disaster recovery of individual databases if there's a regional disaster or a large scale outage. Once geo-replication is set up, you can initiate a geo-failover to a geo-secondary in a different Azure region. The geo-failover is initiated programmatically by the application or manually by the user.
- What it is: Creates up to 4 readable secondary databases in any Azure region.
- RPO/RTO:
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective): Near real-time (typically 5 seconds).
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective): Typically < 30 seconds.
- Failover: Manual failover to a secondary region.
- Use case: Ideal for globally distributed applications requiring fast failover and disaster recovery.
4.2. Auto-Failover Groups
The failover groups feature allows you to manage the replication and failover of some or all databases on a logical server to a logical server in another region
- What it is: Provides automated failover between primary and secondary databases across regions.
- RPO/RTO:
- RPO: Typically 5 seconds.
- RTO: Typically 30 seconds to a few minutes.
- Failover: Automatic failover in case of a regional outage; supports manual failover as well.
- Use case: Suitable for high-availability applications that require both automatic failover and readable secondary databases.
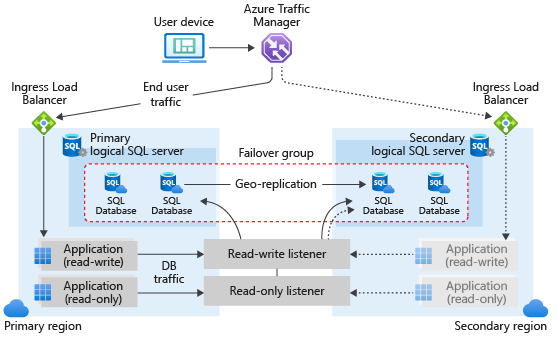
4.3. Zone Redundant Configuration
- What it is: Ensures high availability by distributing the SQL Database replicas across Availability Zones within the same region.
- RPO/RTO:
- RPO: 0 (no data loss).
- RTO: Automatic recovery within the same region (typically less than 30 seconds).
- Failover: Automatic failover between zones in case of a zone failure.
- Use case: Best for applications requiring high availability within a single region without regional disaster recovery needs.
4.4. Point-in-Time Restore
- What it is: Allows restoring a database to any point in time within the retention period (7-35 days).
- RPO/RTO:
- RPO: Determined by backup intervals (up to 1 hour).
- RTO: Depends on the size of the database (can take minutes to hours).
- Failover: No automatic failover; used for accidental data loss or corruption scenarios.
- Use case: Suitable for recovering from user or application errors like accidental deletions or corruption.
4.5. Geo-Restore
- What it is: Restores the database from geo-replicated backups to any region in case of a regional outage.
- RPO/RTO:
- RPO: Up to 1 hour (based on backup frequency).
- RTO: Several hours (depends on the size of the database and network conditions).
- Failover: Manual restoration required.
- Use case: Used for full regional outages when no geo-replicated secondary databases are available.
4.6. Comparisons
| Solution | Protection | RPO | RTO | Failover Type | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Built-in HA (Zone-Redundant) | Within a region (zones) | 0 (no data loss) | < 30 seconds | Automatic failover | Mission-critical apps needing low downtime |
| Built-in HA (Non-Zone-Redundant) | Within a region | 0 (no data loss) | 30 sec to a few minutes | Automatic failover | Applications not requiring zone redundancy |
| Active Geo-Replication | Cross-region (manual) | ~5 seconds | < 30 seconds (manual) | Manual failover | Global apps with read scalability |
| Auto-Failover Groups | Cross-region (automatic) | ~5 seconds | 30 sec to few minutes | Automatic failover | Automatic cross-region DR with read scale |
| Geo-Restore | Cross-region (manual restore) | Up to 1 hour | Several hours | Manual restore | Last-resort, cost-effective DR option |
| Summary: |
- High Availability: Azure SQL Database offers built-in high availability through multiple replicas within a region, with optional zone redundancy for added protection in critical applications.
- Disaster Recovery:
- Active Geo-Replication provides cross-region replication and manual failover.
- Auto-Failover Groups offer cross-region DR with automatic failover and global read scale.
- Geo-Restore is a cost-effective solution for restoring databases in the event of a regional disaster.
High availability by service tier
Ref: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/training/modules/azure-sql-high-availability/4-high-availability-architecture
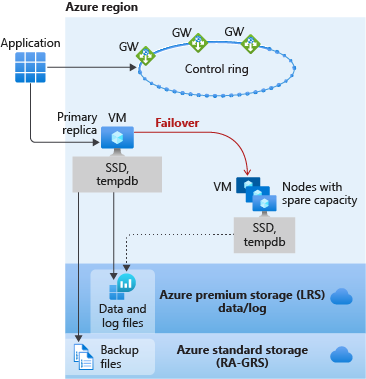
General Purpose
- The primary replica uses locally attached SSD for the
tempdb. - The data and log files are stored in Azure Premium Storage, which is locally redundant storage (multiple copies in one region).
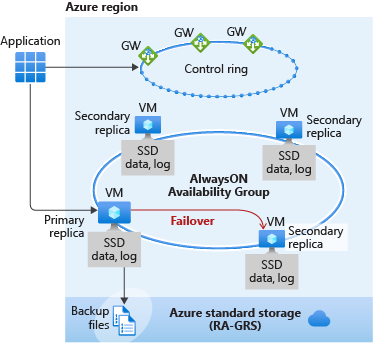
Business Critical
Using Business Critical is like deploying an Always On availability group (AG) behind the scenes. Unlike in the General Purpose tier, the data and log files in Business Critical are all running on a direct-attached SSD, which significantly reduces network latency
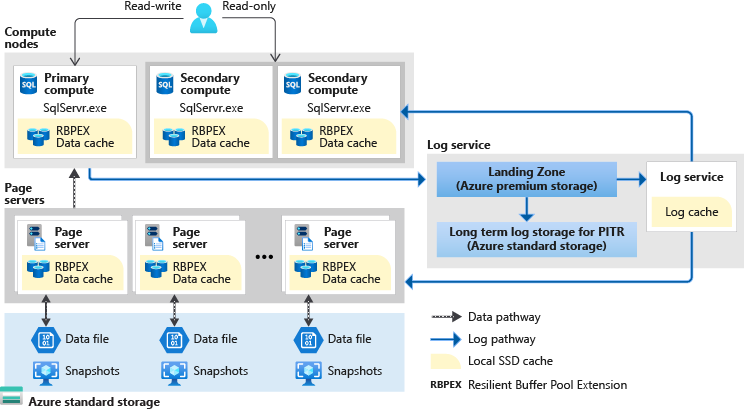
Hyperscale
This service tier uses a tiered layer of caches and page servers to expand the ability to quickly access database pages without having to access the data file directly.
5. Azure SQL Database
An Azure SQL database is a fully managed service. You don't have to deal with complex database tasks like configuring and managing high availability, tuning, and backups. The service automatically upgrades each SQL database to run the most recent version of SQL Server. You get the latest SQL Server capabilities without having to perform manual updates.
-
It's a highly scalable, intelligent, relational database service built for the cloud with the industry's highest availability.
-
SQL Database is the only deployment option that supports scenarios that require large databases (currently up to 100 TB) or autoscaling for unpredictable workloads (serverless).
-
You can create a SQL Database elastic database pool, where all databases in the pool share the same set of compute and storage resources. Each database can use the resources it needs, within the limits you set, depending on current load.
-
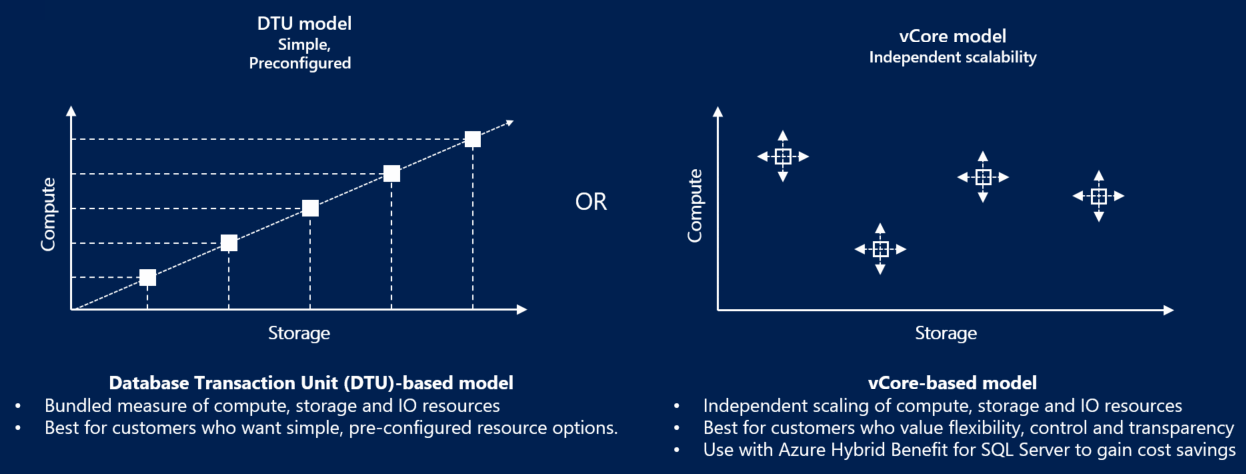
There are two primary pricing options for SQL Database: DTU and vCore. A serverless option is also available for a single database.
-
vCore: A vCore is a virtual core. You choose the number of virtual cores and have greater control over your compute costs. This option supports the Azure Hybrid Benefit for SQL Server and reserved capacity (pay in advance).
-
DTU: A DTU (Database Transaction Unit) is a combined measure of compute, storage, and I/O resources. The DTU option is a simple, preconfigured purchase option.
-
Serverless: A compute tier for single databases in SQL Database. The serverless model automatically scales compute, based on workload demand, and bills only for the amount of compute used.
Consider how Azure SQL Database can be included in your relational data storage plan:
-
Consider vCore pricing. (Microsoft recommended) Select compute and storage resources independently for multiple SQL databases or an elastic database pool. Use Azure Hybrid Benefit for SQL Server or reserved capacity (pay in advance) to save money. You control the compute and storage resources that you create and pay for.
-
Consider DTU pricing. Choose this simple, preconfigured purchase plan for a bundled measure of compute, storage, and I/O resources to support multiple SQL databases. This option isn't available for Azure SQL Managed Instance.
-
Consider serverless option. Use the serverless compute tier for a single SQL database. You're billed only for the amount of compute used.
-
Consider elastic database pools. Buy a set of compute and storage resources to share among all SQL databases in an elastic pool. For more information, see SQL elastic pools.
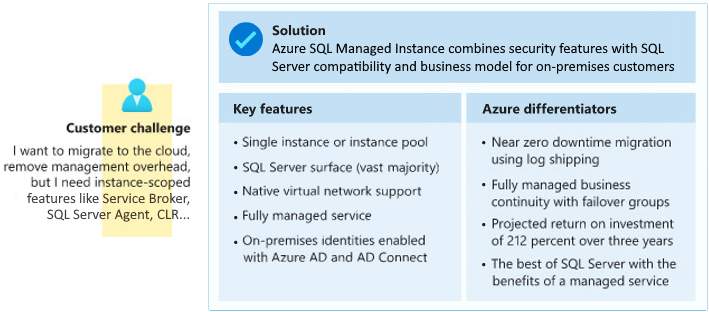
6. Azure SQL Managed Instance
Review the following characteristics of the SQL Managed Instance deployment option:
-
You can use SQL Managed Instance to do lift-and-shift migrations to Azure without having to redesign your applications.
-
Azure SQL Managed Instance is ideal for customers interested in instance-scoped features, such as SQL Server Agent, Common language runtime (CLR), Database Mail, Distributed transactions, and Machine Learning Services.
-
SQL Managed Instance uses vCores mode. You can define the maximum CPU cores and maximum storage allocated to your managed instance. All databases within the managed instance share the resources allocated to the instance.
-
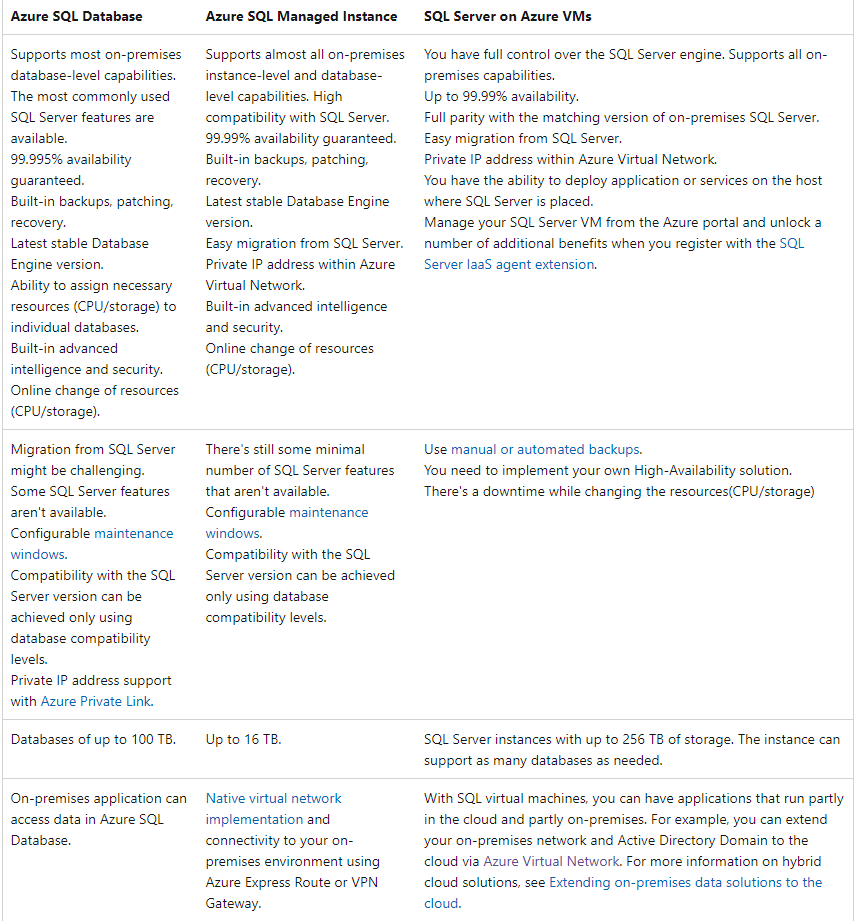
Most of the features available in SQL Server are available in SQL Managed Instance. Review this comparison of SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance.
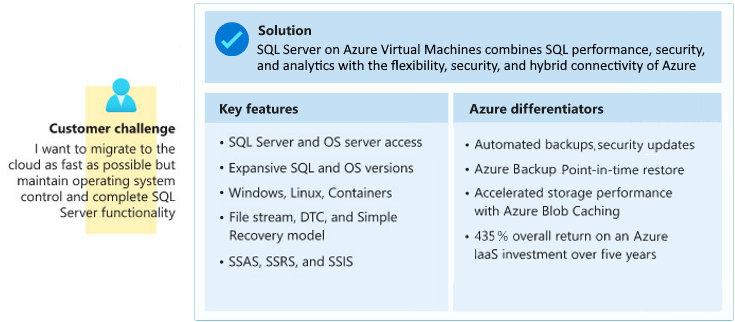
7. SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines
Review the following characteristics of the SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines deployment option:
-
When you run SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines, you have access to the full capabilities of SQL Server.
-
All of your SQL Server skills should directly transfer during the migration, and Azure can help automate backups and security patches.
-
Unlike the Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance deployment options, you're responsible for version update operations for the OS and SQL Server.
7.1. High Availability Solutions
| HA Solution | Protection Level | Failover Type | Automatic Failover | Data Loss (RPO) | Read-Scale Support | Supported Editions | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Always On Availability Groups | Database-level | Manual/Automatic | Yes | 0 (Synchronous), Possible (Async) | Yes (readable secondaries) | Enterprise (basic AG in Standard) | Mission-critical apps with global reach |
| Failover Cluster Instances (FCI) | Instance-level | Automatic | Yes | 0 | No | Standard, Enterprise | Instance-level protection, shared storage |
| Database Mirroring | Database-level | Manual/Automatic | Yes (with witness) | 0 (Synchronous), Possible (Async) | No | Standard, Enterprise (deprecated) | Legacy systems with simple HA needs |
| Log Shipping | Database-level | Manual | No | Possible (depends on log shipping frequency) | No | All Editions | Simple and cost-effective DR solution |
| Replication | Object-level (tables, etc.) | Manual | No | Possible | Yes (read-only replicas) | All Editions | Data distribution and reporting workloads |
Summary:
- Always On Availability Groups (AG) is the most advanced and flexible solution, providing both HA and DR, with the ability to failover automatically or manually and support for read-scale workloads.
- Failover Cluster Instances (FCI) offers instance-level protection and automatic failover, making it ideal for environments with shared storage infrastructure.
- Database Mirroring (though deprecated) is still used in legacy systems for database-level protection, with synchronous and asynchronous options.
- Log Shipping provides a manual, cost-effective solution for DR with potential data loss.
- Replication is more suited for data distribution and reporting, rather than HA.
Each solution caters to different HA requirements based on the criticality of the system, budget, and infrastructure.
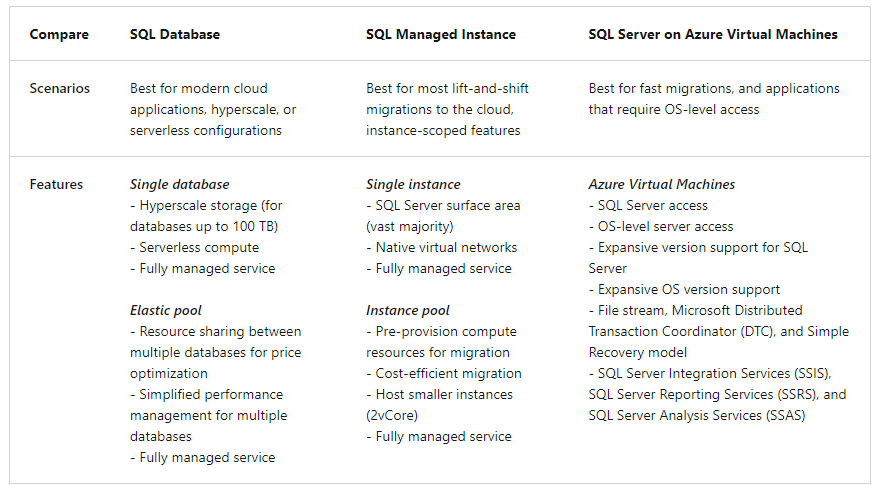
8. Compare Azure SQL deployment options
9. Azure SQL Edge
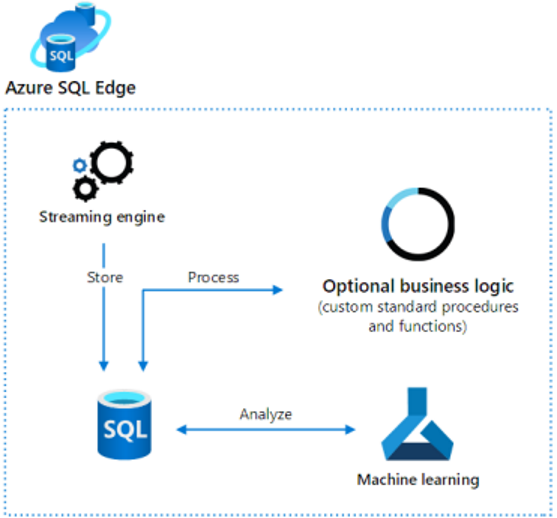
Azure SQL Edge is an optimized relational database engine geared for IoT and IoT Edge deployments. Azure SQL Edge is built on the same engine as SQL Server and Azure SQL. Developers with SQL Server skills can reuse their code to build edge-specific solutions on Azure SQL Edge. Azure SQL Edge provides capabilities to stream, process, and analyze relational and nonrelational data.
- Azure SQL Edge is a containerized Linux application. The startup-memory footprint is less than 500 MB.
- You can design and build apps that run on many IoT devices
- Access a built-in streaming engine to help derive insights from data streams.
10. References
- Azure SQL
- Azure SQL Database
- Azure SQL Managed Instance
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/training/modules/design-data-storage-solution-for-relational-data/7-design-security-for-data-at-rest-data-transmission-data-use
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/training/modules/design-data-storage-solution-for-relational-data/2-design-for-azure-sql-database
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/training/modules/design-data-storage-solution-for-relational-data/3-design-for-azure-sql-managed-instance