Azure Entra ID
1. What is Microsoft Entra ID
Microsoft Entra ID is a cloud-based identity and access management service that your employees can use to access external resources. Example resources include Microsoft 365, the Azure portal, and thousands of other SaaS applications.
2. User management
2.1. Bulk user creation
To use the bulk create operation, download the CSV template file, and copy and paste the details of the users to be created.
Those fields are mandatory: Name, User Name, Initial Password, Block Sign in.
2.2. User properties
There are some Microsoft Entra ID-specific properties like Age group and Usage location that can be edited only in Microsoft Entra ID for either of the two types of users. These properties are unavailable in Active Directory.
2.3. Add a user as Administrator user to all AD devices
To do that, navigate to Microsoft Entra ID -> Devices -> Device Settings and click Manage Additional local administrators on all Microsoft Entra joined devices.
3. Control Plane & Data Plane
There are two types of operations in Azure:
- Control plane operations manage Azure resources. They happen on/to a resource.
- Data plane operations work on data exposed by the Azure resource. They happen within a resource.
4. Lock
- Lock can be created at the subscription, resource group, and resources level.
- Individual resources also inherit the locks from their parent resource group and subscription.
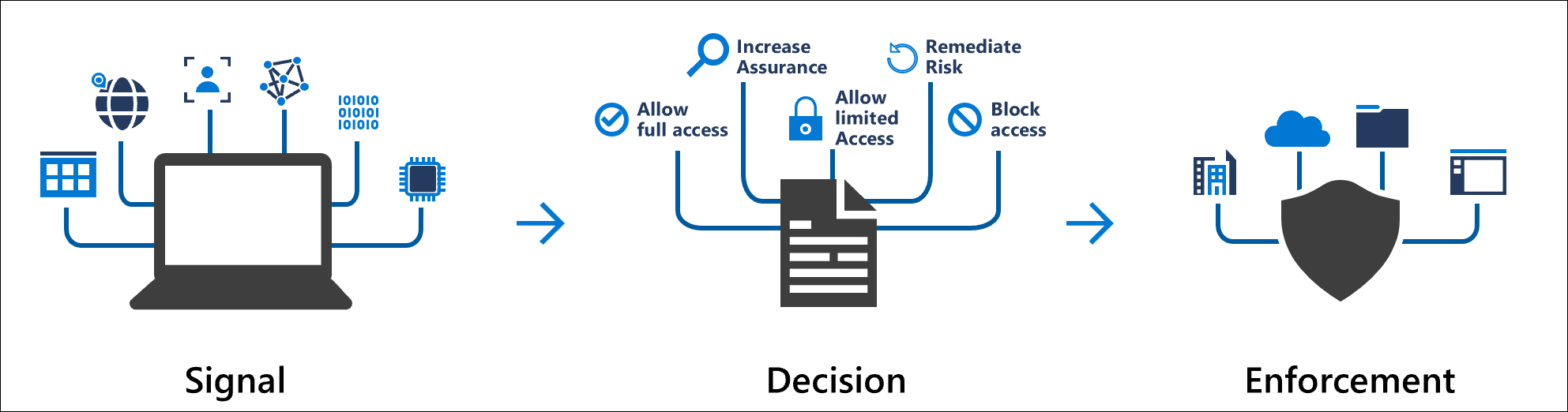
5. Conditional Access policy
Conditional Access policies at their simplest are if-then statements; if a user wants to access a resource, then they must complete an action. For example: If a user wants to access an application or service like Microsoft 365, then they must perform multifactor authentication to gain access.
Conditional Access provides the ability to configure restrictions based on the user/group, application, device state, IP range, and sign-in risk.
5.1. Create policy
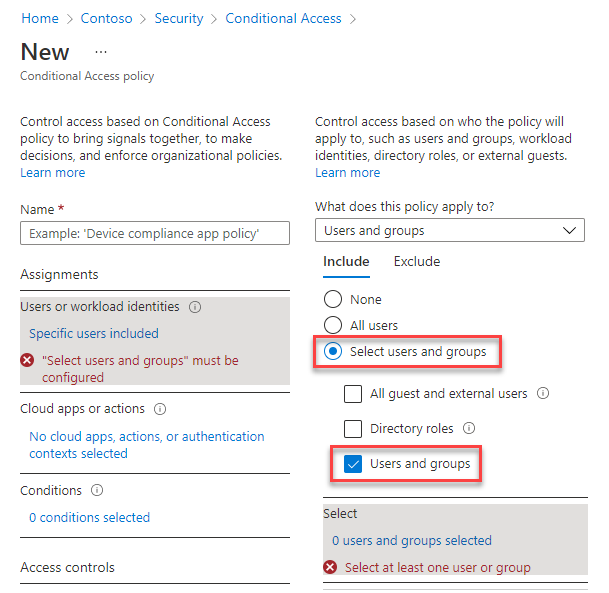
Select the current value under Users or workload identities.
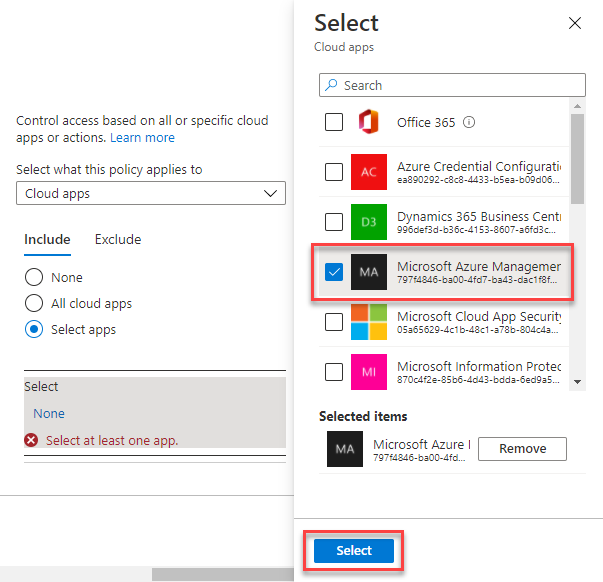
5.2. Configure which apps require multifactor authentication
Select the current value under Cloud apps or actions, and then under Select what this policy applies to, verify that Cloud apps is selected.
You can choose to apply the Conditional Access policy to All cloud apps or Select apps. To provide flexibility, you can also exclude certain apps from the policy.
5.3. Assignments
The assignments portion controls the who, what, and where of the Conditional Access policy.
5.3.1. Users and groups
Users and groups assign who the policy include or exclude when applied. This assignment can include all users, specific groups of users, directory roles, or external guest users.
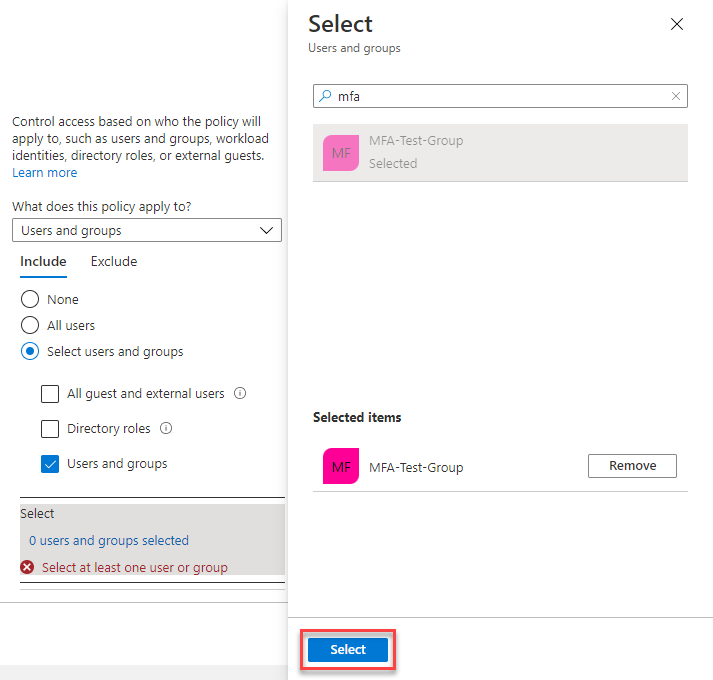
5.3.2. Target resources
Target resources can include or exclude cloud applications, user actions, or authentication contexts that are subjected to the policy.
5.3.3. Network
Network contains IP addresses, geographies, and Global Secure Access' compliant network to Conditional Access policy decisions. Administrators can choose to define locations and mark some as trusted like those for their organization's primary network locations.
5.3.4. Conditions
A policy can contain multiple conditions.
- Sign-in risk
- Device platforms
- Client apps: The software the user is employing to access the cloud app. For example, 'Browser' and 'Mobile apps and desktop clients'. By default, all newly created Conditional Access policies apply to all client app types even if the client apps condition isn't configured.
- Filter for devices: This control allows targeting specific devices based on their attributes in a policy.
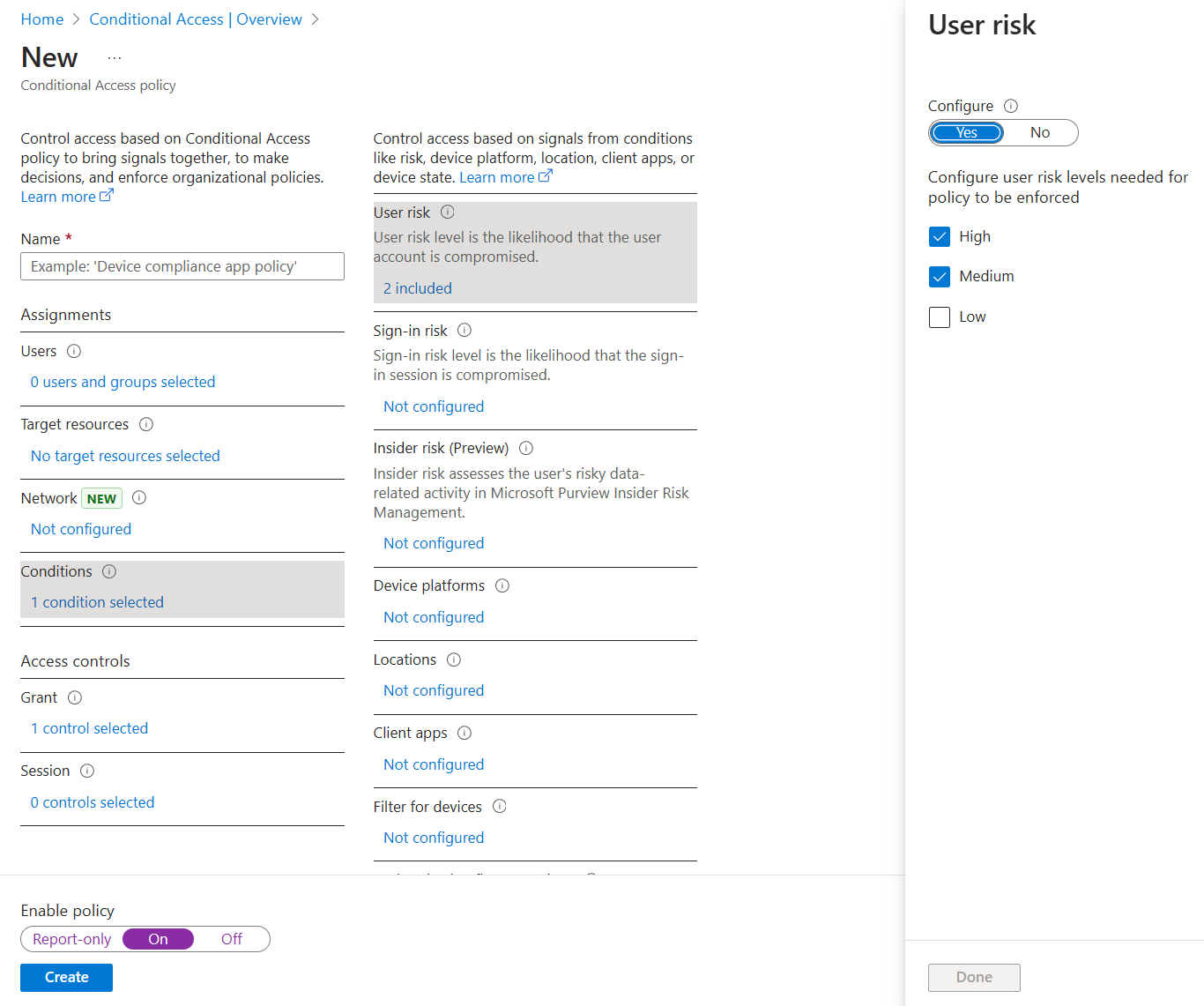
5.4. Access control
5.4.1. Grant control
Within a Conditional Access policy, an administrator can use access controls to grant or block access to resources.
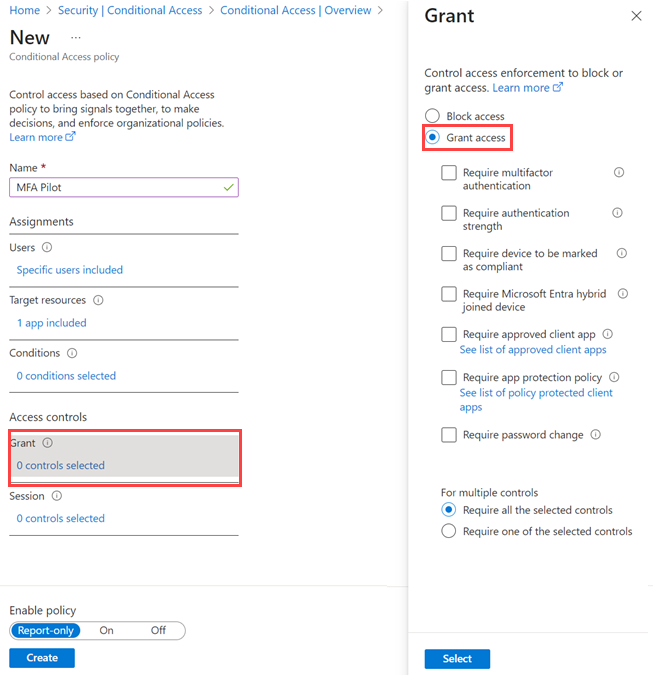
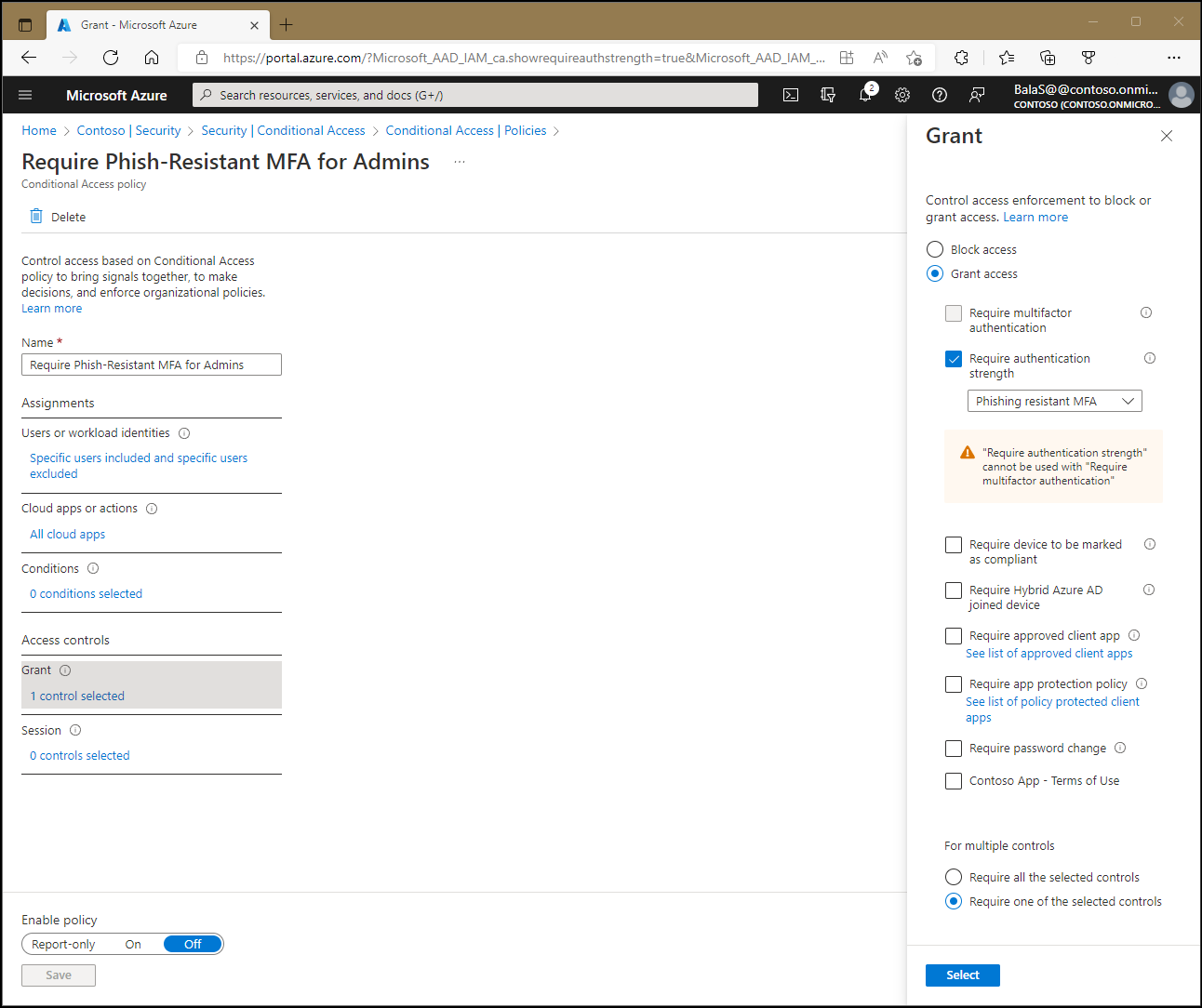
5.4.2. Session control
Within a Conditional Access policy, an administrator can make use of session controls to enable limited experiences within specific cloud applications.
5.5. Activate the policy
Roles
Global Admin VS Owner
Ref: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/answers/questions/1315085/difference-between-global-admin-and-owner-in-micro
Azure AD Global Admin is a Directory level role, however Global Admin have a privilege to elevate their access to Azure subscription and deployed resources. On other had Owner is an Azure RBAC roles specifically to get access to resources deployed within Azure Subscription. I would like to share following details with you with regards to each role.
Global Admin Azure AD Role:
- Users with this role have access to all administrative features in Azure Active Directory, as well as services that use Azure Active Directory identities like the Microsoft 365 Defender portal, the Microsoft Purview compliance portal, Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, and Skype for Business Online.
- Global Administrators can view Directory Activity logs.
- Furthermore, Global Administrators can elevate their access to manage all Azure subscriptions and management groups.
- This allows Global Administrators to get full access to all Azure resources using the respective Azure AD Tenant.
- For more details please review: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/roles/permissions-reference#global-administrator
Azure RBAC Owner
- Grants full access to manage all resources, including the ability to assign roles in Azure RBAC.
- This role is associated with Azure resources, such as resource groups or individual resources (e.g., virtual machines, storage accounts).
- An Owner has full access to manage and control all aspects of the resources within the scope they are assigned.
- The Owner role is specific to a particular resource or resource group and does not have privileges over the Azure AD tenant as a whole.
- For more details please review: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/role-based-access-control/built-in-roles#owner
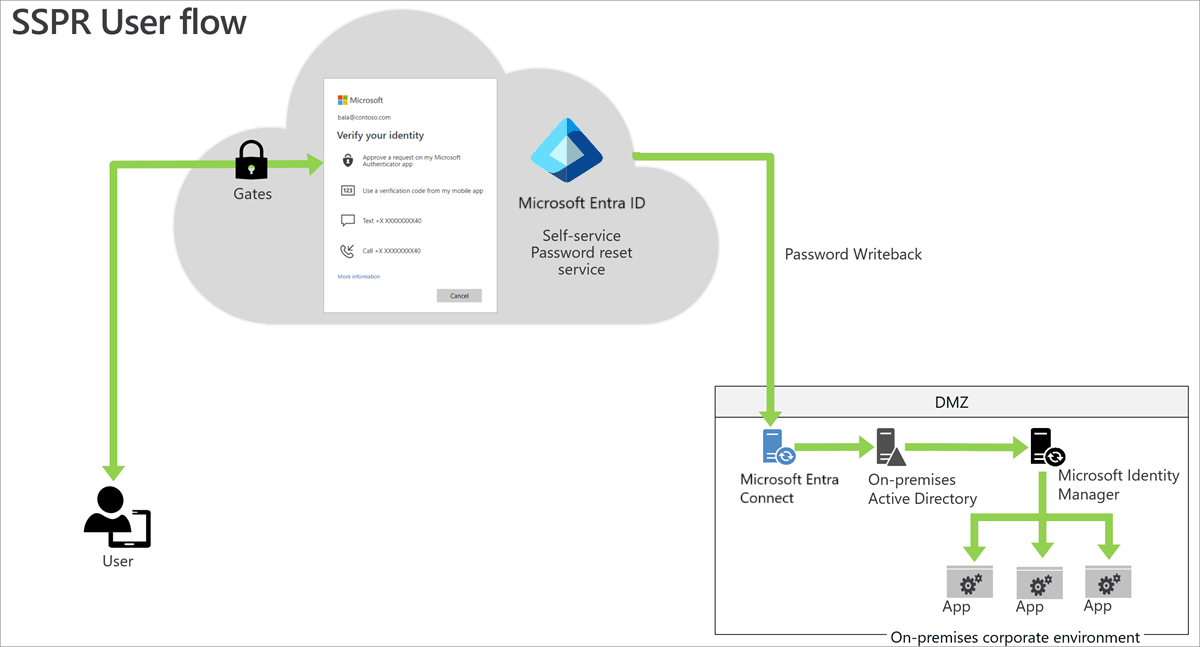
Configure self-service password reset
- A Microsoft Entra ID P1 license is required for password reset
Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is a service in Microsoft Entra ID that enables you to manage, control, and monitor access to important resources in your organization.
Key features: - Provide just-in-time privileged access to Microsoft Entra ID and Azure resources - Assign time-bound access to resources using start and end dates - Require approval to activate privileged roles - Enforce multifactor authentication to activate any role - Use justification to understand why users activate - Get notifications when privileged roles are activated - Conduct access reviews to ensure users still need roles - Download audit history for internal or external audit - Prevents removal of the last active Global Administrator and Privileged Role Administrator role assignments
6. References
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity/
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity/authentication/tutorial-enable-azure-mfa