Azure Storage Account
1. Types of storage accounts
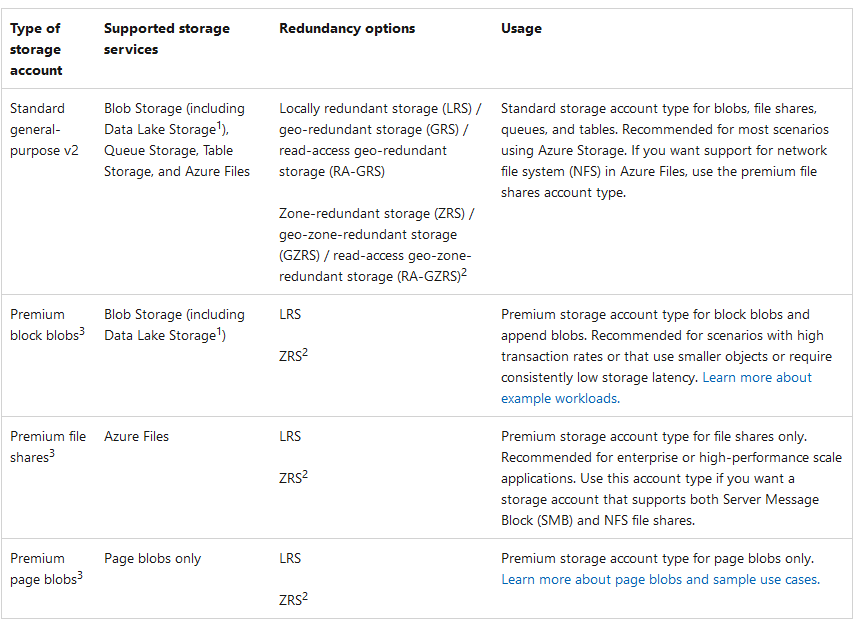
2. Life cycle
- Lifecycle management policies are supported only for block blobs and append blobs in general-purpose 2, premium block blob, and Blob storage account.
- Not supported for page blobs and file shares.
- A premium storage account that supports only page blobs. Hence, Lifecycle management is not supported.
- Lifecycle management doesn't affect system containers such as the $web, $log
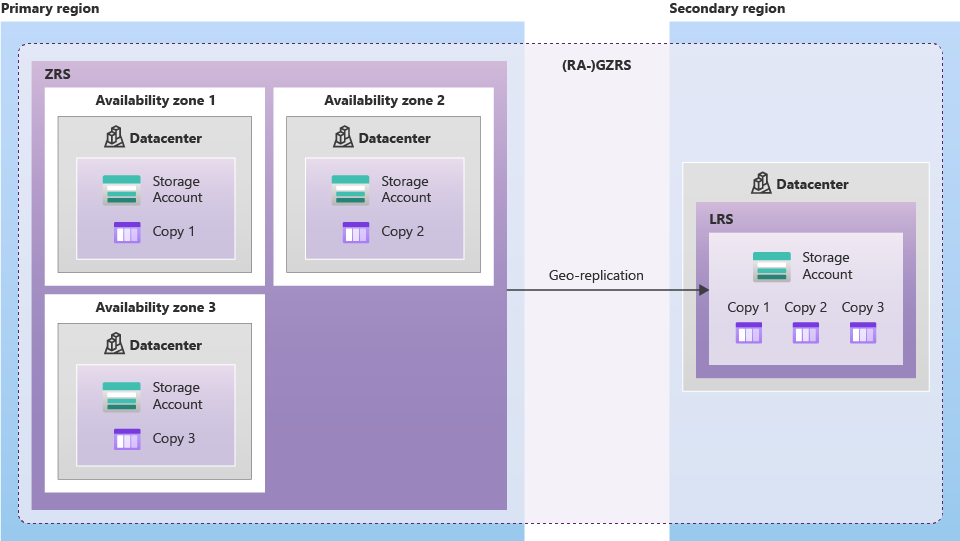
3. Redundancy
- Adding or removing between geo-replication (between LRS, GRS, RA-GRS OR between (ZRS, GZRS, RA-GZRS)) can be done on Azure Portal.
- Adding or removing zone redundancy needs a support ticket, for example: LRS <-> ZRS.

3.1. LRS
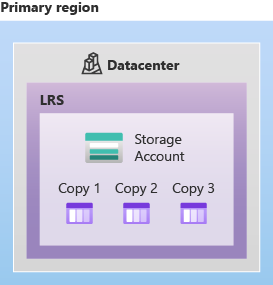
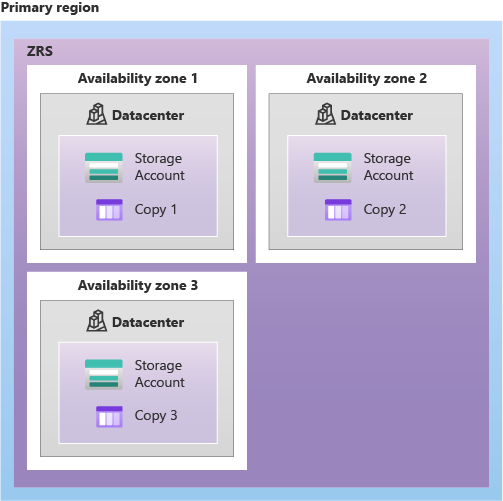
3.2. ZRS
3.3. RA-GRS
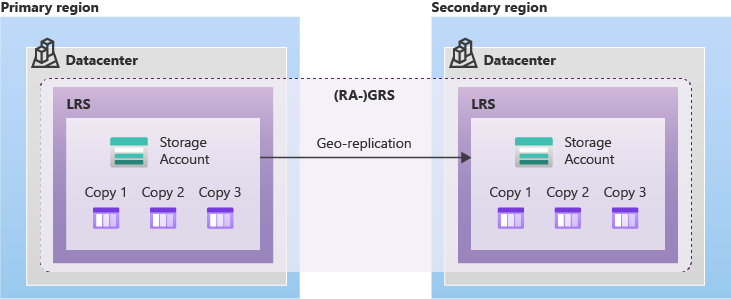
3.4. RA-GZRS
4. Object replication
- Object replication asynchronously copies block blobs in a container according to rules that you configure. The contents of the blob, any versions associated with the blob, and the blob's metadata and properties are all copied from the source container to the destination container.
- Object replication requires that the following Azure Storage features are also enabled:
- Blob versioning: Must be enabled on both the source and destination accounts so that any state changes to the previously replicated blobs in the source are easily preserved in the target.
- Change feed: Must be enabled on the source account so that Azure Storage can check the source feed for any change events (write or delete operations) that it would asynchronously replicate to the target account.
- Object replication is supported for general-purpose v2 storage accounts and premium block blob accounts.
- Object replication supports block blobs only; append blobs and page blobs aren't supported.
- Object replication isn't supported for blobs in the source account that are encrypted with a customer-provided key.
- Customer-managed failover isn't supported for either the source or the destination account in an object replication policy. Reference Link: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/object-replication-overview#prerequisites-and-caveats-for-object-replication
5. SAS token
-
A shared access signature (SAS) is a URI that grants restricted access rights to Azure Storage resources. You can provide a shared access signature to clients who shouldn't be trusted with your storage account key but who need access to certain storage account resources. By distributing a SAS URI to these clients, you can grant them access to a resource for a specified period of time, with a specified set of permissions.
-
Note: When a user accesses blob data, the Azure portal checks if the user’s role has permission (
Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listkeys/action) to read storage account keys. If the user's role has this permission, the portal uses the keys to grant access to blob data. That’s how theOwnerandContributorroles, which do not have any permissions in theDataActionssection (in its role definition), can access the blob data (they haveMicrosoft.Storage/*in the Actions section).
6. Stored access policy
- A stored access policy provides an additional level of control over service-level shared access signatures (SASs) on the server side. Establishing a stored access policy serves to group shared access signatures and to provide additional restrictions for signatures that are bound by the policy.
- You can use a stored access policy to change the start time, expiry time, or permissions for a signature. You can also use a stored access policy to revoke a signature after it has been issued.
- The following storage resources support stored access policies: Blob containers, File shares, Queues, Tables
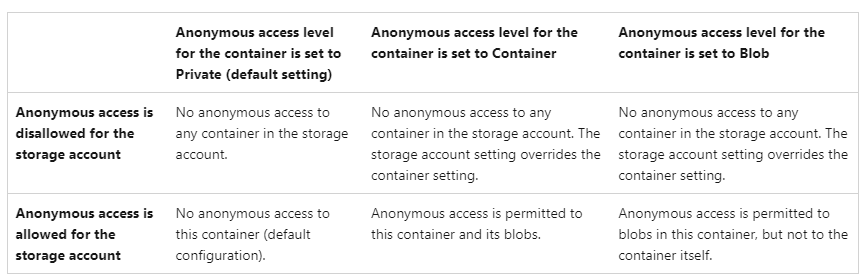
7. Public Access Level

- Container: Any user can read the containers and the blobs anonymously (even without any explicit permissions). Any user can connect to the container with a Container access level via Azure Storage Explorer and read the blobs within those containers.
- Blob: any user can read only the blobs, not the containers anonymously. Unless you have permissions (either via Microsoft Entra ID, or storage account keys, or SAS), you cannot connect to a container with a Blob access level in Azure Storage Explorer.
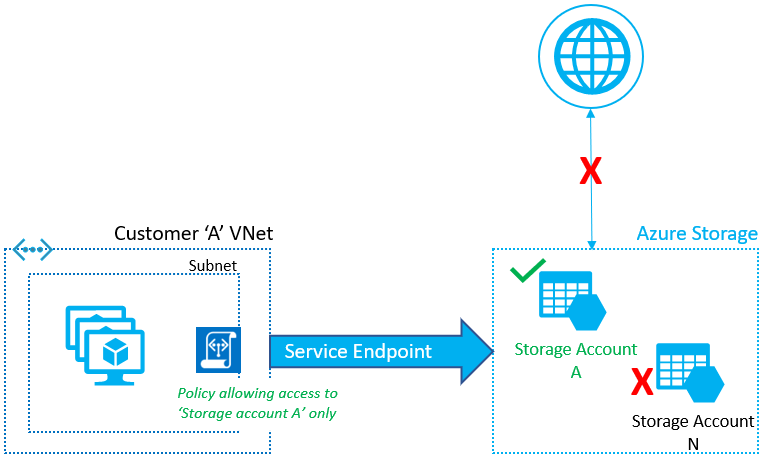
8. Virtual network service endpoint policies for Azure Storage
Virtual Network service endpoint policies allow you to filter egress virtual network traffic to Azure Storage accounts over service endpoint, and allow data exfiltration to only specific Azure Storage accounts. Endpoint policies provide granular access control for virtual network traffic to Azure Storage when connecting over service endpoint.
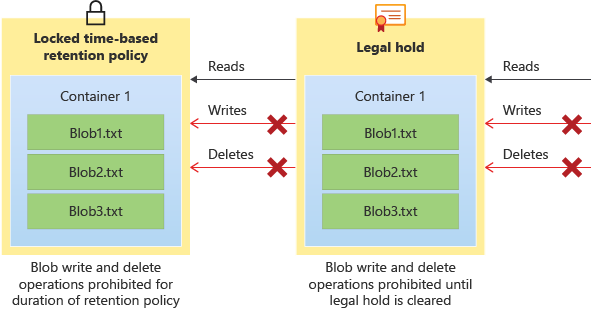
9. Immutable storage
Immutable storage for Azure Blob Storage supports two types of immutability policies:
-
Time-based retention policies: With a time-based retention policy, users can set policies to store data for a specified interval. When a time-based retention policy is set, objects can be created and read, but not modified or deleted. After the retention period has expired, objects can be deleted but not overwritten.
-
Legal hold policies: A legal hold stores immutable data until the legal hold is explicitly cleared. When a legal hold is set, objects can be created and read, but not modified or deleted.
 Ref: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/immutable-storage-overview
Ref: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/immutable-storage-overview
10. AZCopy tool
- AzCopy is available on all major operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- The currently supported version of the AzCopy tool enables you to copy data only between file shares and blobs, not even tables.
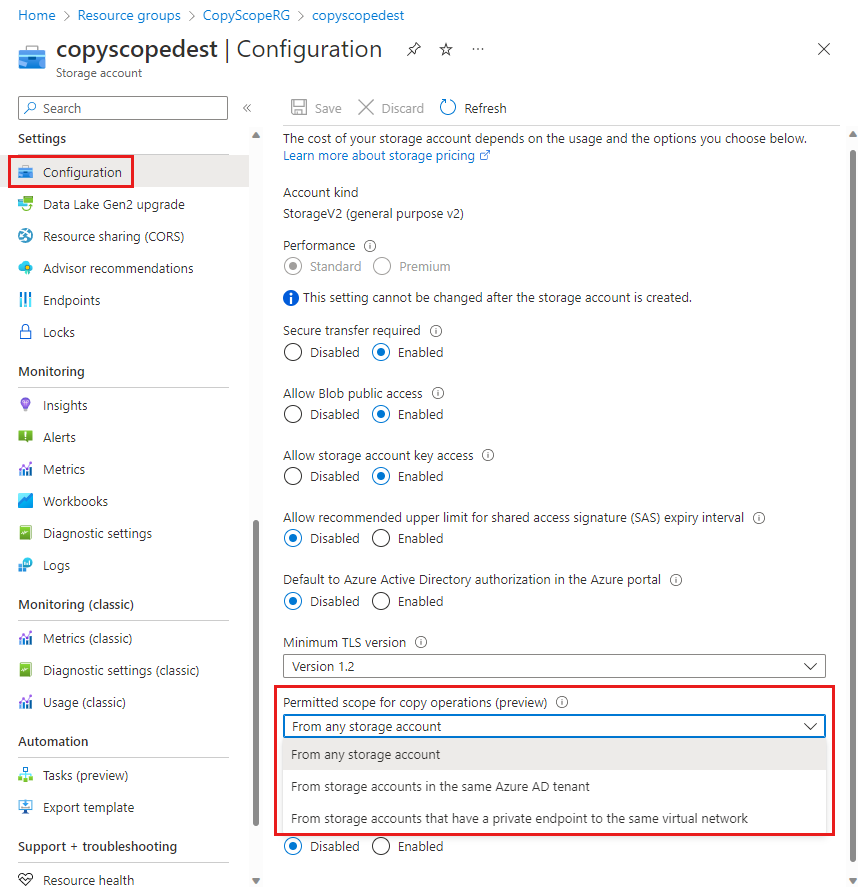
11. Copy across tenant
- In order to have a copy operation across Microsoft Entra ID tenants to be successful, you need to set the Permitted scope for copy operations as From any storage account on the target storage account.
12. deleteRetentionPolicy & containerDeleteRetentionPolicy
- In the given ARM template, the deleteRetentionPolicy and containerDeleteRetentionPolicy indicate the number of days that the deleted items should be retained in the soft-delete state.
13. References
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/
END